Why CellChek XL
CellChek XL™ - clinical specular microscope system
20 Second exam
The CellChek XL specular microscope represents the latest in endothelial cell analysis, algorithms, and computer technology. Enhanced with auto-focus, auto-alignment, and auto-cell counting, the CellChek XL easily captures consistent, high quality images of your corneal endothelium using a patented method that identifies the position of the cellular interface.
Powerful multi-point, analytic detail
The CellChek XL offers five fixation points for image capture at the center and four peripheral sites, allowing a more comprehensive look at the cornea. This is particularly valuable in cases such as keratoconus | corneal transplantations, DSAEK, CXL, or the presence of corneal dystrophies such as Fuch's corneal dystrophy.
Location specific data samples
Unique to the CellChek XL, the CellChek™ software automatically records the location from which the data samples were acquired. One strong value of specular microscopy is to be able to assess and quantify change in the cornea over time. Without location data,trending is simply not accurate or reliable.
Specular microscopes are used for endothelial analysis, both for routine clinical practice and clinical research.
Using non-contact optical pachymetry, the CellChek XL provides corneal thickness measurements at all five data sample sites. Now all patients over 18 years of age will have base line readings established.
Non-contact corneal thickness measurements
Why Endothelial Analysis?
Why it is quite simple
Standard biomicroscopy does not provide the critical detail of the earliest signs of endothelial disease even though we use Haag Streit Biomicroscopes . CellChek XK allows us 100 x more magnification. We just see every thing.
Standard biomicroscopy does not provide the critical detail of the earliest signs of endothelial disease even though we use Haag Streit Biomicroscopes . CellChek XK allows us 100 x more magnification. We just see every thing.

Clinical Indications
- Evaluation of abnormal corneal signs or symptoms
- Treatment of known ophthalmic diseases
- Treatment of known ophthalmic injury
- Preoperative assessment of surgical risk

CellChek XL™ - clinical specular microscope system
20 Second exam
The CellChek XL specular microscope represents the latest in endothelial cell analysis, algorithms, and computer technology. Enhanced with auto-focus, auto-alignment, and auto-cell counting, the CellChek XL easily captures consistent, high quality images of your corneal endothelium using a patented method that identifies the position of the cellular interface.
Powerful multi-point, analytic detail
The CellChek XL offers five fixation points for image capture at the center and four peripheral sites, allowing a more comprehensive look at the cornea. This is particularly valuable in cases such as keratoconus | corneal transplantations, DSAEK, CXL, or the presence of corneal dystrophies such as Fuch's corneal dystrophy.
Location specific data samples
Unique to the CellChek XL, the CellChek™ software automatically records the location from which the data samples were acquired. One strong value of specular microscopy is to be able to assess and quantify change in the cornea over time. Without location data,trending is simply not accurate or reliable.
Specular microscopes are used for endothelial analysis, both for routine clinical practice and clinical research.
Using non-contact optical pachymetry, the CellChek XL provides corneal thickness measurements at all five data sample sites. Now all patients over 18 years of age will have base line readings established.
Non-contact corneal thickness measurements
20 Second exam
The CellChek XL specular microscope represents the latest in endothelial cell analysis, algorithms, and computer technology. Enhanced with auto-focus, auto-alignment, and auto-cell counting, the CellChek XL easily captures consistent, high quality images of your corneal endothelium using a patented method that identifies the position of the cellular interface.
Powerful multi-point, analytic detail
The CellChek XL offers five fixation points for image capture at the center and four peripheral sites, allowing a more comprehensive look at the cornea. This is particularly valuable in cases such as keratoconus | corneal transplantations, DSAEK, CXL, or the presence of corneal dystrophies such as Fuch's corneal dystrophy.
Location specific data samples
Unique to the CellChek XL, the CellChek™ software automatically records the location from which the data samples were acquired. One strong value of specular microscopy is to be able to assess and quantify change in the cornea over time. Without location data,trending is simply not accurate or reliable.
Specular microscopes are used for endothelial analysis, both for routine clinical practice and clinical research.
Using non-contact optical pachymetry, the CellChek XL provides corneal thickness measurements at all five data sample sites. Now all patients over 18 years of age will have base line readings established.
Non-contact corneal thickness measurements

YOUR CLINICAL PROCEDURE AT THE SPECTRUM EYE CENTRE
- WE will document any disease process
- We will show you and educate you
- We will aid in planning any treatment of a disease process
- We will document the delivery of any medical treatment
- We will document the response to medical treatment
Specular Microscopy Basics
- Cell density (ECD)
- Cell size variation
- Cell shape variation
- Corneal thickness (pachymetry)
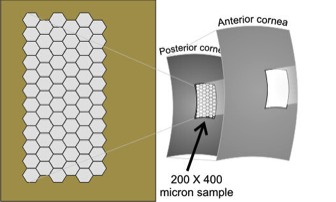
- Specular reflection of the endothelium - aqueous interface
- High definition, 440x microscopic view of endothelial morphology
- Easy and automated focus, alignment, capture of data
- Auto-cell counting + patented Center Method analysis
- Robust detailed analytics
- Position data of sample to assess change over time
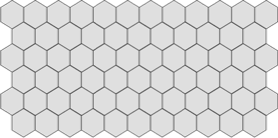
Normal Endothelial Cell Density (ECD)
Normal ECD declines with age
Normal ECD declines with age
Low ECD
Low ECD is a risk factor for cataract and corneal surgeries that can be missed without the use of specular microscopy.
Low ECD is a risk factor for cataract and corneal surgeries that can be missed without the use of specular microscopy.
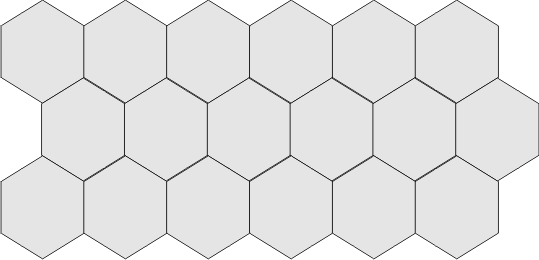
Polymegethism
Change from uniform cell sizes to variable cell sizes is an indication of distress to the endothelium.
Change from uniform cell sizes to variable cell sizes is an indication of distress to the endothelium.
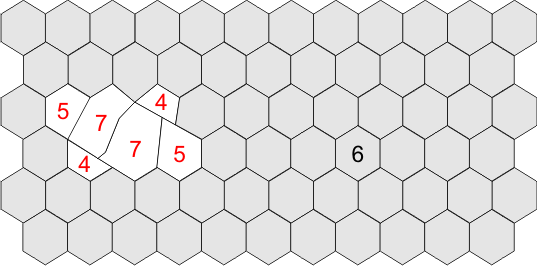
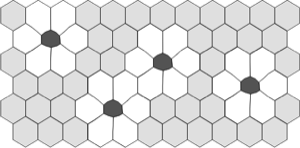
Pleomorphism
Change from optimum hexagonal cell geometry to variable / compromised cell shapes.
Change from optimum hexagonal cell geometry to variable / compromised cell shapes.
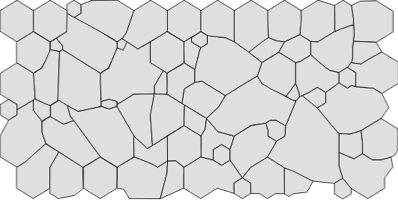
Normal ECD with Polymegethism and Pleomorphism
Here the ECD is typical, but there are also large changes in morphology with high variance in cell area / sizes (pleomorphism) and a large number of non-hexagonal cell shapes (4, 5, 7 sided cells, ie. pleomorphism). A cell count without cellular morphology statistics may be misleading.
Here the ECD is typical, but there are also large changes in morphology with high variance in cell area / sizes (pleomorphism) and a large number of non-hexagonal cell shapes (4, 5, 7 sided cells, ie. pleomorphism). A cell count without cellular morphology statistics may be misleading.




